Based on the immense proliferation of data in today's market environment, a business is in a relentless search for ways and means to forecast trends, consumer behavior patterns, etc. Terms such as predictive analytics and artificial intelligence (AI) come up frequently in these discussions, and they are often considered synonymous. This raises an important question: Is predictive analytics part of artificial intelligence, or are they two different approaches yet related solutions?
To answer this, we must explore their definitions, methodologies, and areas of overlap while examining their real-world applications.
What is Artificial Intelligence?
Defining Artificial Intelligence
AI is the ability to create systems that operate and learn like the human brain does. These tasks include learning from data, reasoning, problem-solving, and understanding natural language. AI encompasses a broad spectrum of technologies, such as:
- Machine Learning (ML): Broadly refers to systems that improve their performance in data processing tasks without requiring redesign.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): The process by which machines can read, comprehend, and produce human speech.
- Computer Vision: Software programs that can decipher images and videos in particular.
- Robotics and Automation: Mechanized equipment that is able to perform human tasks purposefully.
Artificial intelligence is the prerogative of intelligent systems that aim at emulating the human brain in order to support organizations in the elimination of bureaucratic practices and the achievement of valuable strategies and insights within a short amount of time.
What is Predictive Analytics?
The Beginning of the Predictive Analytics Era
Business analytics, or specifically predictive business analytics, involves analyzing historical data to identify future trends. The main purpose is to analyze data in order to forecast future transformations and tendencies in the process.
For example:
- Analyses insights are employed to make likely inventory rates for the retailers.
- Loan risks for banks are estimated according to the creditworthiness of customers.
- Through patient factors, healthcare organizations can forecast disease outbreaks.
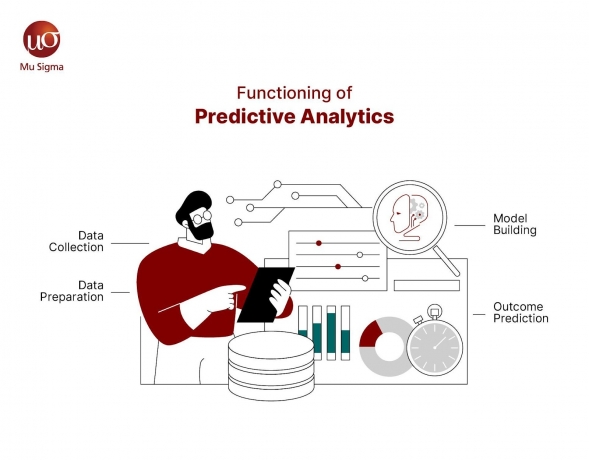
The Functioning of Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics relies on:
- Data Collection: Collecting archival information from different information sources.
- Data Preparation: The process of preparing, formatting, and arranging data or the conditions for analysis.
- Model Building: Classification of data through the development of hypotheses and repeating experiments to see if they bear any relationship to the data.
- Outcome Prediction: Using the models to forecast probabilities or results for probable situations that will occur in the future.
The Relationship between Artificial Intelligence and Predictive Analysis
Overlap and Distinction
Predictive analytics and artificial intelligence share significant overlap but differ in their scope and application:
Overlap:
- Predictive analytics frequently employs machine learning, which is a part of artificial intelligence. For instance, improved analytical models may incorporate artificial neural networks, which are an AI approach, to recognize diverse patterns in customer behaviour.
- Predictive analytics is a widespread technique in AI systems as it helps them to predict particular events and automate their responses to them.
Distinction:
- Artificial Intelligence is broader, encompassing various capabilities like automation, language understanding, and visual recognition, alongside prediction.
- Predictive analytics focuses solely on forecasting outcomes based on historical data and statistical models, which can function independently of AI.
While predictive analytics can exist without AI, its integration with AI significantly enhances its capabilities, enabling dynamic and adaptive models that evolve with new data.
The Role of Machine Learning in Predictive Analytics
Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence and other related abilities such as automation, natural language processing, computer vision, in addition to predictions.
Predictive analytics is primarily embedded in the objectives of making decisions based on statistical patterns and historical data, meaning that it does not necessarily require the integration of AI into a firm.
Despite being one term capable of being used independently, its incorporation with AI is a major plus, as it gives the predictive analytics model the ability to learn and change as new data comes in.
As predictive analytics evolved and machine learning became more sophisticated, the combination of these two disciplines offered tremendous potential for results.
Predictive analytics is most significantly driven by the machine component of artificial intelligence. Unlike the conventional statistical models, which assume a certain number of probable outcomes, machine learning models increase their efficacy with every new data set.
Examples of Machine Learning in Predictive Analytics:
- Regression Models: Forecasting values of continuous types of variables such as sales growth or, indeed temperature.
- Classification Models: Categorizing data, such as identifying fraudulent transactions.
- Clustering: Basing customer segmentation on buying habits for marketing.
These machine learning techniques make predictive analytics no longer give fixed predictions but real-time ones.
Real-World Applications: AI-Driven Predictive Analytics
Creating a New Customer Experience
By combining artificial intelligence with predictive analytics, businesses can
- Predict customer tendencies to target marketing communications to users individually. This is the key to customer churn management.
- Help to improve areas of managing and foreseeing the demand and stocks.
For instance, in online shopping, it is estimated that AI-driven predictive analysis helps create recommendations that boost conversion rates by 15-20%.
Revolutionizing Healthcare
The integration of AI with predictive analytics has transformed healthcare:
- The process involves using patient details and other relevant details to determine disease outbreaks.
- Prediction of the treatment of patients is crucial for devising individualized care provision.
- The digitization of health care services for purposes of faster identification of patients at risk of being readmitted to the hospital.
Enhancing Financial Risk Management
In the financial sector, artificial intelligence-enabled predictive analytics is used to:
- The identification of fraudulent transactions with a level of near real-time.
- Understand credit risks to approve credit facilities.
- Identify market movements for the investment Arizona decisions.
Key Differences Between Artificial Intelligence and Predictive Analytics
| Aspect | Artificial Intelligence | Predictive Analytics |
| Scope | Broad: Includes machine learning, NLP, robotics, and more. | Narrow: Focuses on data-driven predictions. |
| Dependency | Can incorporate predictive analytics as a tool. | May or may not rely on AI techniques. |
| Functionality | Encompasses automation, decision-making, and prediction. | Primarily used for forecasting future events. |
While the two are interdependent in many use cases, they serve distinct roles in solving business challenges.
Final Thoughts: The Synergy Between AI and Predictive Analytics
To answer the central question, indeed, sometimes it is a subset of artificial intelligence but can also work independently in other applications. Together, it is a force multiplier that provides unique value by providing timely, real-time, accurate data that can be leveraged by businesses.
Businesses that incorporate predictive analytics through artificial intelligence are likely bound to become more nimble, automated, and creative in today's market environment. In the future, as these technologies are developed further, their implementations will change the process by which organizations make decisions on data.